Employees of the Institute of Biophysics, the National Oncology Center and the Italian Institute of Nanotechnology published articles in a prestigious journal in Q1
The staff of the Institute of Biophysics of the Ministry of Science and Education of the Republic of Azerbaijan, corresponding member of ANAS Oktay Gasimov, and researcher Matanat Bakhishova, in collaboration with the Institute of Nanotechnology (CNR) in Italy (D. Simeone and others), as well as the academic staff of the National Oncology Center of Azerbaijan, academician Jamil Aliyev and Elkhan Kazimov, have published a joint paper titled “Tailoring Gold Nanoisland-Based Biosensors for Ultrasensitive Detection of Doxorubicin in Biological Fluids” in the prestigious journal "ACS Applied Nano Materials" (ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 16, 18724–18736, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.4c01827), which is included in Q1 (IF= 5.3, SiteScore= 8.3).
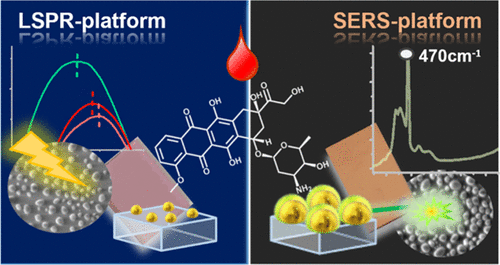
The main goal of the work presented in the paper is to contribute to "Personalized Medicine," which is a key priority in modern medicine worldwide. Through Personalized Medicine, it is possible to determine specific physiological parameters for each patient and to select the most appropriate and effective treatment methods. The dosage and duration of drug therapy should be personalized to increase the drug's efficacy while minimizing side effects. In other words, precision medicine involves therapeutic drug monitoring to determine the concentration of the drug in plasma and to optimize the dosage range accordingly. The paper focuses on the monitoring of Doxorubicin (DOX), a drug used in cancer treatment that has serious side effects, in blood plasma.
To achieve this, an ultra-sensitive biosensor capable of detecting DOX in blood plasma was developed. The classical biosensor based on Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR) can detect DOX in the nanomolar range, while a new type of nanostructured biosensor, composed of core/shell Au/Al2O3 nanoislands, can detect the drug in the picomolar range.
In the application of biosensors in various in-vitro systems, it was possible to detect DOX with high sensitivity. Subsequently, these biosensors were used to monitor the time-dependent changes of the drug in a patient undergoing treatment at the National Oncology Center, and successful results were obtained.